In this article, we’ll explore 10 critical networking protocols, their functionalities, and practical applications. Plus, we’ll dive into Python code examples to help you get hands-on experience.
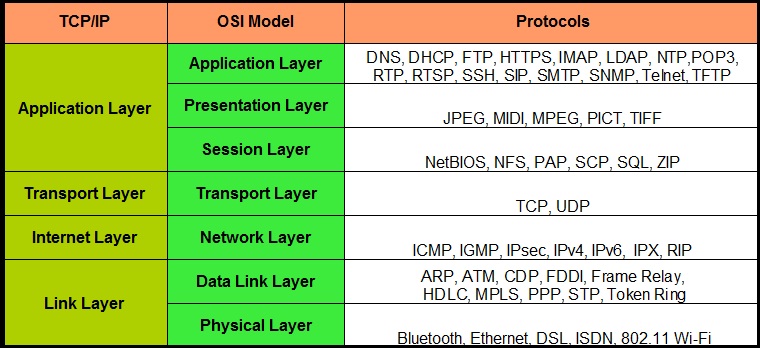
TCP/IP
The TCP/IP suite is the cornerstone of internet communication, encompassing a range of protocols that work together to ensure reliable data transmission.
Key Protocols in TCP/IP
- IP (Internet Protocol): Manages addressing and routing of data packets.
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): Provides reliable, connection-oriented data transfer.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol): Offers fast, connectionless data transfer, ideal for real-time applications.
TCP vs. UDP: When to Use Each
- TCP: Use for applications requiring reliable data transfer, such as email and web browsing.
- UDP: Ideal for speed-sensitive applications like online gaming and live streaming.
TCP Python Example
import socket
HOST = 'localhost'
PORT = 65432
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.bind((HOST, PORT))
s.listen()
conn, addr = s.accept()
with conn:
print(f"Connected by {addr}")
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024)
if not data:
break
print(f"Received data: {data.decode()}")
conn.sendall(b"Hello from the server!")HTTP(S)
HTTP is the backbone of web communication, facilitating the exchange of content between web browsers and servers. HTTPS adds a layer of security by encrypting data traffic.
Applications of HTTP
- Web Browsing: Enables users to access and interact with web content.
- Web APIs: Facilitates data exchange between applications.
- RESTful Services: Supports resource identification and access across services.
HTTP Python Example
import requests
url = "https://www.example.com"
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(response.text)
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")DNS
DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, acting as the internet’s phonebook.
Importance of DNS
- Ease of Use: Simplifies access to websites using memorable domain names.
- Scalability: Efficiently routes traffic across the internet.
- Flexibility: Easily updates records to point to different servers.
DNS Python Example
import socket
domain_name = "www.google.com"
try:
ip_address = socket.gethostbyname(domain_name)
print(f"IP address of {domain_name}: {ip_address}")
except socket.gaierror:
print("DNS resolution failed")DHCP
DHCP automates the assignment of IP addresses to devices on a network, simplifying network management.
Applications of DHCP
- Simplified Management: Automates IP configuration.
- Scalability: Easily handles large networks.
- Flexibility: Supports dynamic IP allocation.
DHCP Python Example
# Note: This is a conceptual example. Actual DHCP client implementation would be more complex.
import subprocess
result = subprocess.run(["dhclient", "-v"], capture_output=True, text=True)
print(result.stdout)FTP
FTP enables the transfer of files between computers on a network, supporting efficient file sharing and management.
Applications of FTP
- File Sharing: Facilitates easy exchange of files.
- Website Management: Used for uploading and managing website content.
- Backup and Archiving: Centralizes data backup and storage.
FTP Python Example
from ftplib import FTP
ftp = FTP("ftp.example.com")
ftp.login("username", "password")
with open("local_filename.txt", "rb") as file:
ftp.storbinary("STOR remote_filename.txt", file)
ftp.quit()SSH
SSH provides secure remote access to systems, enabling secure command execution and file transfer.
Applications of SSH
- Remote Administration: Manages systems remotely.
- Secure File Transfer: Transfers files securely.
- Command Execution: Runs commands on remote systems.
SSH Python Example
import paramiko
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect("ssh.example.com", username="username", password="password")
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command("ls -l")
print(stdout.read().decode())
ssh.close()SMTP and POP3
SMTP and POP3 are essential for email communication, with SMTP handling sending and POP3 managing retrieval.
Applications of SMTP and POP3
- Email Communication: Enables sending and receiving emails.
- Webmail Integration: Powers services like Gmail and Outlook.
- Email Automation: Automates email sending tasks.
SMTP Python Example
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
msg = MIMEText("This is the email body content.", "plain")
msg["Subject"] = "This is a test email"
msg["From"] = "your_email@example.com"
msg["To"] = "recipient@example.com"
with smtplib.SMTP("smtp.example.com", 587) as server:
server.starttls()
server.login("your_email@example.com", "your_password")
server.send_message(msg)
print("Email sent successfully!")ICMP
ICMP is used for network diagnostics, with tools like ping and traceroute leveraging its capabilities.
Applications of ICMP
- Ping: Tests connectivity between devices.
- Traceroute: Identifies the path packets take through the network.
- Error Reporting: Reports errors during data transmission.
ICMP Python Example
import os
target_host = "8.8.8.8"
response = os.system(f"ping -c 1 {target_host}")
if response == 0:
print(f"Ping to {target_host} successful!")
else:
print(f"Ping to {target_host} failed.")SNMP
SNMP enables the monitoring and management of network devices, supporting performance tracking and configuration.
Applications of SNMP
- Network Monitoring: Tracks device performance and health.
- Configuration Management: Manages device settings remotely.
- Fault Detection: Identifies and reports network issues.
SNMP Python Example
from pysnmp.hlapi import *
errorIndication, errorStatus, errorIndex, varBinds = next(
getCmd(SnmpEngine(),
CommunityData('public'),
UdpTransportTarget(('192.168.1.1', 161)),
ContextData(),
ObjectType(ObjectIdentity('SNMPv2-MIB', 'sysDescr', 0)))
)
if errorIndication:
print(errorIndication)
elif errorStatus:
print(f"{errorStatus.prettyPrint()} at {errorIndex and varBinds[int(errorIndex)-1][0] or '?'}")
else:
for varBind in varBinds:
print(f"{varBind[0]} = {varBind[1]}")DNSSEC
DNSSEC adds security to DNS, protecting against attacks like DNS spoofing and ensuring data integrity.
Applications of DNSSEC
- Prevention of DNS Spoofing: Protects against malicious redirection.
- Data Integrity: Ensures DNS records are not tampered with.
- Secure Transactions: Critical for online banking and e-commerce.
DNSSEC Python Example
# Note: DNSSEC validation typically involves more complex setup and libraries like dnspython.
# This is a conceptual example.
import dns.resolver
resolver = dns.resolver.Resolver()
resolver.use_dnssec = True
try:
answers = resolver.resolve("www.example.com", "A")
for rdata in answers:
print(rdata.address)
except dns.resolver.NoAnswer:
print("DNSSEC validation failed or no answer received")Conclusion
These 10 protocols form the backbone of modern networking, providing the foundation for secure, reliable, and efficient data transmission. By mastering these protocols, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how networks operate and open doors to exciting career opportunities in the tech industry.
Understanding these protocols is just the beginning. As you continue your journey, you’ll encounter more specialized protocols tailored to specific applications and technologies. So, dive in, explore, and embrace the fascinating world of networking!